ICCT (International Council on Clean Transportation) published a report, focusing on ships trading with the European Union, predicts a tripling of demand for LNG as marine fuel between 2019 and 2030, based on trends in fuel consumption.
The idea that liquefied natural gas (LNG) can help mitigate the climate impacts of the maritime shipping sector rests on the assumptions that ships can switch to bio and e-LNG (“renewable” LNG) in the future and that switching would result in low greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. For this to happen, there must be enough renewable LNG to meet future demand and using it must result in a substantial reduction in GHG emissions on a life-cycle basis compared to fossil LNG. Understanding whether these assumptions are realistic is important for policymakers, including in the European Union, which has committed to reducing its GHG emissions by at least 55% below 1990 levels by 2030 (that is equivalent to a 41% reduction from 2019 levels).
The report also estimates that renewable LNG will cost seven times more than fossil LNG in 2030 and, therefore, subsidies or other policies would be needed to encourage its use.
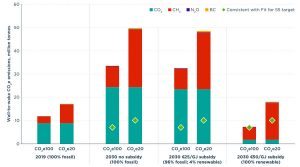
The well-to-wake (WTW) carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions associated with three 2030 scenarios in the European Union are shown in the figure above. Compare the scenario in which ships use 100% renewable LNG in 2030 (far right, representing a €50 per gigajoule subsidy) to emissions from using 100% fossil in 2019 (far left). As shown, using renewable LNG could cut WTW CO2e emissions by 38% based on 100-year global warming potentials (GWP, labeled as CO2e100) but raise emissions 6% based on 20-year GWP (CO2e20) because of methane’s strong near-term warming effects. Focusing on the orange portions of the bars, even using 100% renewable LNG doubles methane emissions compared to 2019; this is primarily because of methane slip from marine engines.
For renewable LNG to significantly contribute to achieving climate goals, methane slip from marine engines needs to be virtually eliminated and methane leaks upstream need to be greatly reduced. Additionally, methane leaks from onboard fuel tanks and cargo tanks, which researchers are still working to adequately quantify, would need to be near zero. It is important for policymakers and stakeholders to understand that other fuels, including synthetic diesel and green methanol, could offer low life-cycle emissions without the methane problem.
Source ICCT
