NTSB: Poor BRM Caused Allision With Uncharted Offshore Platform
August 25, 2022 Maritime Safety News
The NTSB has released its final report on the allision of a bulker with a decommissioned offshore platform off the coast of Louisiana last year. Its investigators determined that poor bridge resource management and a charting error were the root causes of the casualty.
On Jan. 7, 2021, the bulker Ocean Princess struck the oil and gas platform SP-83A some 24 miles south of Pilottown, Louisiana. No pollution or injuries were reported, and damage to the vessel and platform came to about $1.5 million.
The Ocean Princess offloaded a cargo of ore and steel in New Orleans in late December. On January 6, she was drifting in the Gulf of Mexico before heading back up river to load a cargo of grain. The master planned to drift through the night with the engine on 15-minute standby, keeping clear of traffic and the three platforms located in the area.
In order to give the crewmembers some rest time after a long day of cleaning cargo holds, the master scheduled himself on the bridge, joining the second officer. The vessel was drifting at about 2-3 knots in a northerly direction, with on and off rain showers periodically limiting visibility.
As the watch went on into the early hours of January 7, the master and second officer worked on administrative tasks on the bridge. At about 0100 hours, the vessel drifted towards a fairway, and they called the engine room to prepare to maneuver. With the master at the helm, they headed away from the fairway at a slow bell. At 0113, as he maneuvered away, the master saw a dim yellow light and checked the radar, which was set at a range of about 1.5-3 miles. The second officer had a look and confirmed that the contact was a platform, but could not determine the range visually. It looked like an ENC-charted platform some 5-6 miles away, and they concluded that it was not a hazard.
They were mistaken, and the master only fully appreciated the risk about 40 seconds before contact. Last-minute maneuvers were not successful and the bulker allided with the platform at four knots. The starboard anchor lodged in the platform structure, and the bulker swung on the anchor chain until morning when it could be safely cut free.
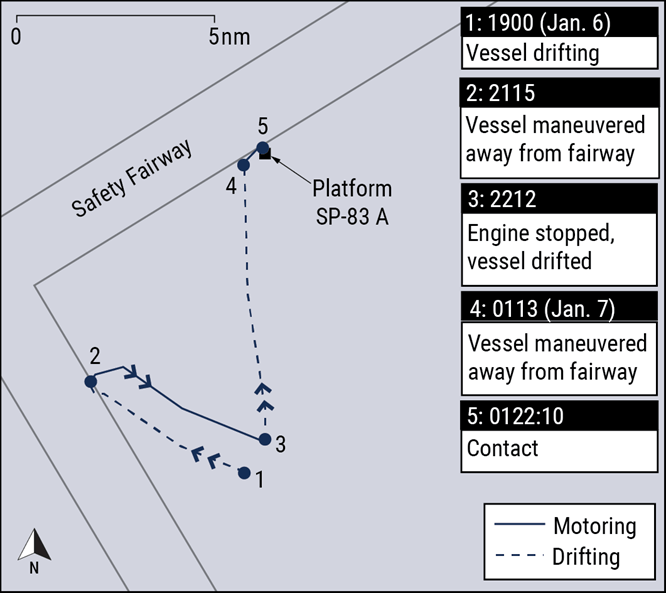
Ocean Princess’ trackline in the hours leading up to the allision (NTSB)
The master and second officer told NTSB that they never saw SP-83A on the radar. After the contact, they found that the platform was properly marked on the paper chart (an Admiralty product) – but SP-83A did not appear on their ECDIS ENC (a NOAA product).
NTSB verified that platform SP-83A was not charted on the official U.S. charts that fed Ocean Princess’ ECDIS. It had been charted correctly at platform commissioning in 1990 but was removed from the NOAA charts in 2010 for unknown reasons. Its absence went unnoticed and uncorrected until the allision. (After the accident, NOAA added it back in.)
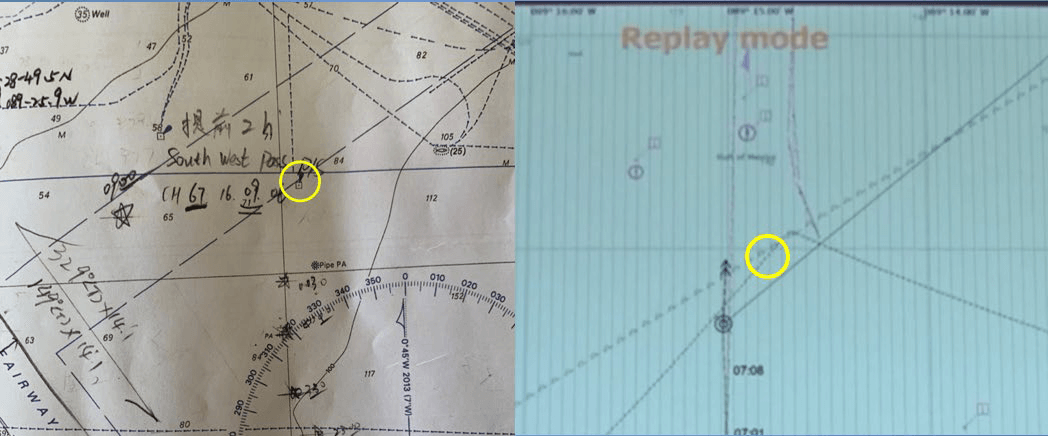
A photo of the British Admiralty chart 3857 (left) and ECDIS screenshot from the Ocean Princess fed by NOAA ENCs (right), which were up to date at the time of the casualty. The British Admiralty chart shows SP-83A, but the ECDIS image shows nothing at that position. (NTSB)
NTSB determined that poor BRM was the probable cause of the casualty, since the bridge team noticed the platform’s lights 10 minutes in advance but failed to take timely and effective action. The platform’s absence from the ENC was a contributing factor.
“Technology, such as an ECDIS, can result in operator overreliance and overconfidence that degrades sound navigation practices and negatively affects situational awareness,” advised NTSB. “When identifying hazards, bridge teams should avoid overreliance on a single data source.”
Source: https://www.maritime-executive.com/article/ntsb-poor-brm-caused-allision-with-uncharted-offshore-platform






